25 December 2019
Two studies recently presented at the recent San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium focused on a subtype of breast cancer known as Her2/neu over-expressed, which include up to 20% of breast cancers. In these tumors, the gene that codes for the Her2 protein receptor has more than the usual number of copies. These tumors tend to have more aggressive growth patterns and up until the development of targeted antibody therapy, prognosis was very poor.
Targeted antibody therapy including trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) is now standard of care for Her2 breast cancers, even in the setting of early-stage disease. Trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla, T-DM1) is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC, a combination of the antibody and a chemotherapy agent) and is most commonly used in patients with metastatic disease. Unfortunately, not all Her2 tumors respond to therapy, and some tumors that initially respond can mutate and become resistant to therapy. Brain metastases can occur in up to 50% of patients with metastatic Her2 breast cancer, and can be challenging to treat as medications may not be able to pass through the blood-brain barrier to get to the cancer cells.
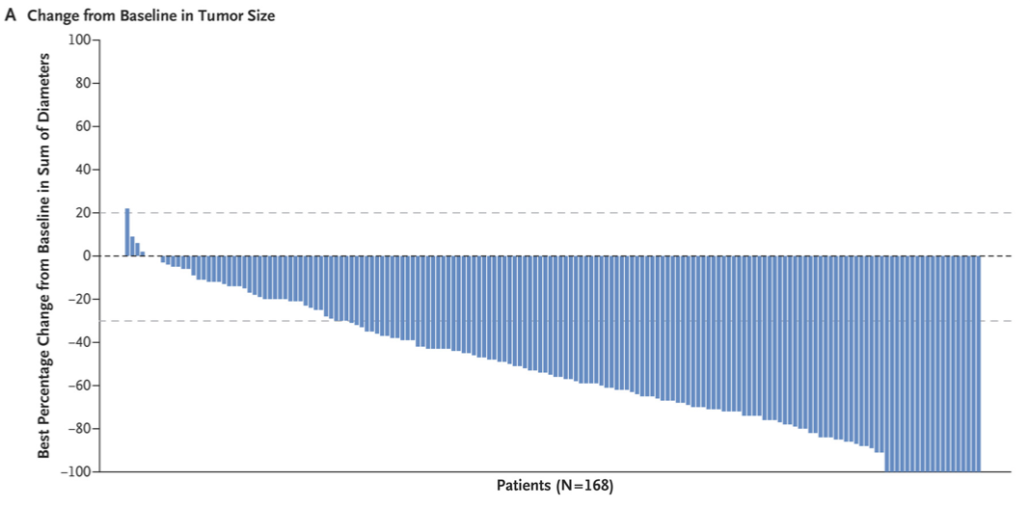
Trastuzumab deruxtecan (DS-8201, Enhertu) is an ADC and results of a phase 2 study (DESTINY-Breast01*) were presented. This study included 184 patients with metastatic Her2 breast cancer, who were experiencing disease progression after receiving 2 or more different anti-Her2 treatment protocols (including trastuzumab emtansine, median 6 prior therapies, range 2-27). This was an “open label” study and patients were not randomized. Median follow up was 11 months and findings included:
- Median treatment duration was 10 months
- Overall response rate was 60.3% (at least 2 follow up scans, 6 weeks apart)
- 11 patients (6%) experienced a complete response (apparent resolution of disease)
- 101 patients (55%) experienced a partial response
- Median duration of response to treatment was 14.8 months
- In patients with brain metastases (24 patients), median progression-free survival (PFS, time to disease advancement) was 18 months
- Adverse events (AE) occurred in all but one patient. The most common AE were nausea, hair loss, vomiting, constipation and neutropenia (low white blood cell count)
- 57% of patients experienced more serious (≥ grade 3) AE
- 28.8% of patients stopped treatment due to disease progression
- 15.2% of patients stopped treatment due to AE
- One of the more serious complications, interstitial lung disease (ILD), was reported in 25 patients and 4 patients died due to ILD-related causes
Shortly after the study was presented, the drug received accelerated FDA approval for patients with unresectable (not able to be removed with surgery) or metastatic Her2 breast cancer who have experienced disease progression after treatment with 2 or more targeted agents. The approval is accompanied by a warning due to risks of ILD as well as embryo-fetal toxicity.
ASCO Post coverage of trastuzumab deruxtecan
The other study involved Tucatinib, which is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, administered in pill form. The Her2CLIMB trial* was a Phase 3 study that included patients with Her2 metastatic breast cancer who previously received treatment with trastuzumab, pertuzumab, and trastuzumab emtansine. Patients with and without brain metastases, including untreated brain metastases, were included. Patients in this trial received either tucatinib or placebo, in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine (Xeloda – an oral form of chemotherapy).
The study included 612 patients. 410 received tucatinib-trastuzumab-capecitabine (T-C) and 202 received placebo-trastuzumab-capecitabine (P-C). 48% of patients in the T-C group and 46% of patients in the P-C group had brain metastases at enrollment. Median follow up was 14 months and findings included:
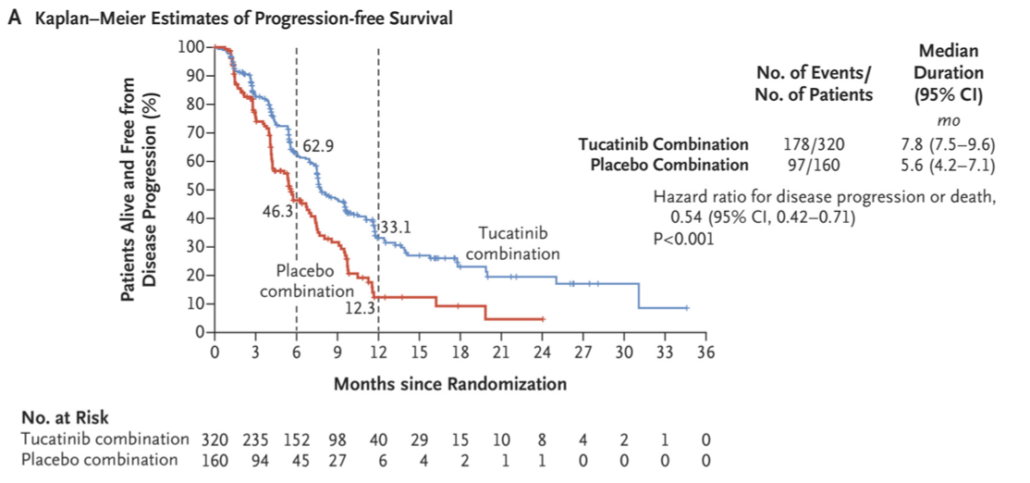
- At one year, PFS was 33% in the T-C group and 12% in the P-C group
- At one year, median duration of PFS was 7.8 months in the patients who received T-C and 5.6 months in the patients who received P-C
- Overall survival (OS) at 2 years was 45% in the patients receiving T-C and 27% in those who received P-C
- Median OS was 21.9 months in the patients receiving T-C and 17.4 moths in the patients who received P-C
- Among patients with brain metastases, estimated PFS at one year was 24.9% in the T-C group and 0% in the P-C group
- Among patients with brain metastases, median duration of PFS was 7.6 months in the T-C group and 5.4 months in the P-C group
- The most common adverse effects in the patients in the T-C group were diarrhea, hand-foot syndrome, nausea, fatigue, and vomiting
- 23 (5.7%) patients in the T-C arm and 6 (3.0%) patients in the P-C arm discontinued therapy due to side effects
- Of the 215 deaths that occurred during the study, the most common reason was disease progression. Adverse events were the cause of death in 6 (1.5%) of patients in the T-C group and 5 (2.5%) in the P-C group
ASCO Post coverage of tucatinib
While these 2 studies demonstrate the progress that has been made in treating an aggressive form of breast cancer, they also serve as a sobering reminder of the work that remains. The hope with targeted therapy is that cancer cells will be killed with minimal toxicity to other cells or the person – we are not quite there yet. In addition, while the improvements in progression free and overall survival is encouraging, we are not yet able to ensure long-term survival for patients with metastatic Her2 breast cancer. If you donate to breast cancer research organizations, please consider this when deciding which groups to support.
*If you are not able to access the full studies and would like a copy, please email me: contact at drattai dot com